The Blockchain Revolution: Unlocking the Power of Decentralization
Technology
Published on 18-07-2023

Just like Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning, Blockchain is one of the most sought-after technologies of today. It redefines how we store, update, and move data. It has the potential to revolutionize any business that holds structured data.
Data security, transparency, and trust are crucial for businesses and individuals in the digital age. Enter blockchain technology, a revolutionary concept that has disrupted numerous industries by introducing decentralized and immutable systems. Blockchain is famous nowadays due to its application in cryptocurrency (Bitcoin Framework).
- Bitcoin became the first application of Blockchain Technology.
- Satoshi Nakamoto formed the Bitcoin Genesis block in 2009.
- Bitcoin is recognized as a digital currency (the electronic equivalent of cash in a banking system)
- Problems in scalability, interoperability, and speed
- Bitcoin: one of the slowest cryptocurrencies, taking about 10 mins to confirm a transaction
- Vitalik Buterin releases Ethereum white paper in 2013
- Genesis block in Ethereum was created in 2015.
- Ethereum required lesser energy to maintain and had less than optimal speed.
- Arrival of Hyperledger from the Linux Foundation and Decentralized Applications (Dapps) of Ethereum
- Focus was to bring greater interoperability and boost network speeds.
- A scaled Blockchain is expected to accelerate processing speeds without sacrificing security.
- Business-oriented hybrid Blockchain projects
- Integration with IoT, AI, and Big Data
Need HELP?
Consult with Expert Now
A blockchain is a distributed ledger that stores transactional records, also known as ‘blocks,’ in several databases known as ‘chains,’ in a network connected through peer-to-peer nodes. Frequently this storage is referred to as a ‘digital ledger.’
To understand blockchain, we must know the terms that are used while referring to a blockchain network or a part of it:

- Distributed: Network configuration where every participant can communicate with one another without going through a centralized point.
- Replicated: Involves sharing information to ensure consistency between redundant resources, such as software and hardware components.
- Peer-to-peer network: Interconnected nodes or peers share resources amongst each other without any centralized administrative system (as exists in Client-Server Network).
- Cryptocurrency: Derived from the words ‘crypto,’ meaning concealed or secret, and ‘currency,’ indicating a system of money.
- Node: An electronic device (computers, mobile devices, servers, etc.) connected to the Internet. All nodes in the network have a copy of the Blockchain ledger and are interconnected.
- Wallet: A digital wallet that allows users to manage cryptocurrency like bitcoin, ether, etc.
- Nonce: Number generated randomly that can be used once in cryptographic communication. Makes a transaction unique to avoid duplicate transactions.
- Hash: The hash function can take data of any size, perform an operation on it, and return a ‘hash,’ i.e., data of a fixed size.
- Mining: Mechanism by which transactions are validated and added to the Blockchain ledger.
- Consensus Protocol: Set of rules to validate all transactions before being added to the Blockchain.
- Blocks In Blockchain: A block is the smallest unit in the Blockchain that records all the transactions.
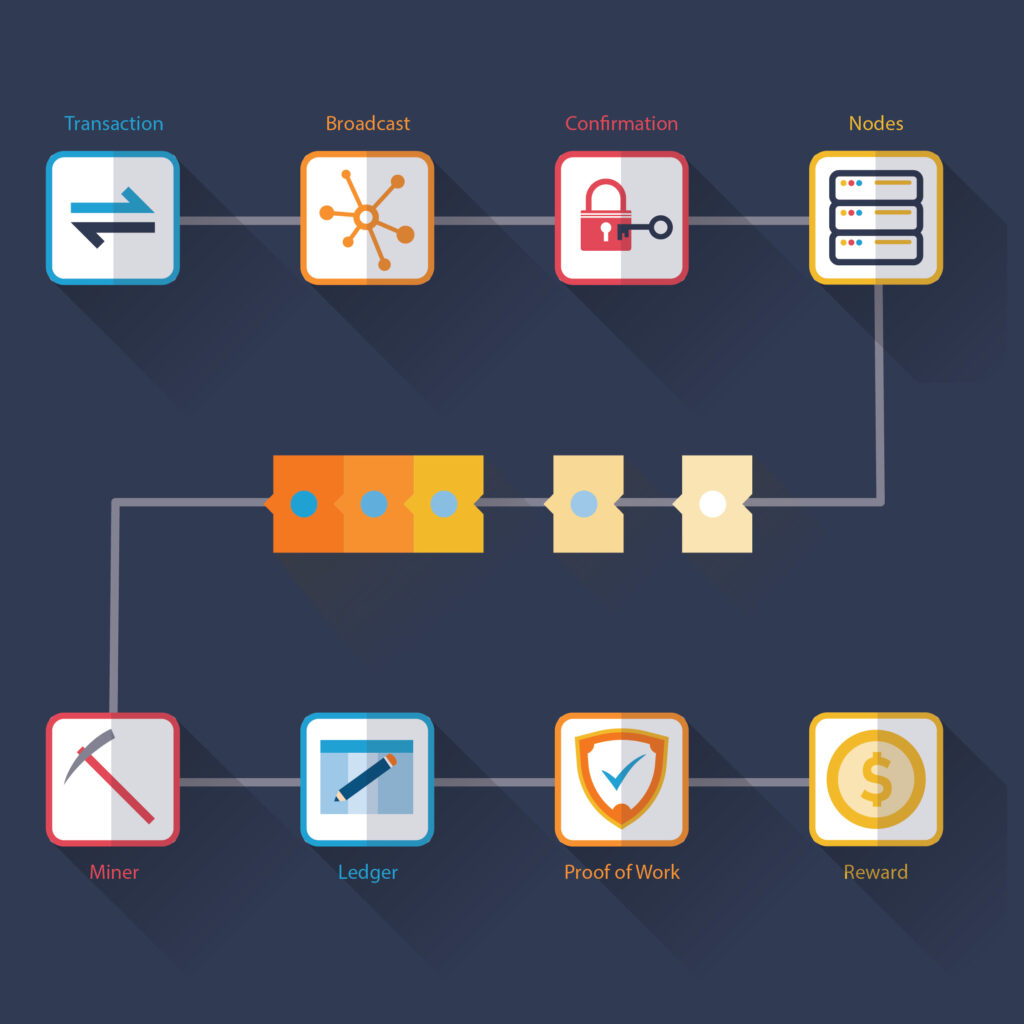
- A node in the blockchain network requests a transaction via a wallet.
- Transaction is broadcasted to all nodes in the network.
- The network validates and verifies transactions using a consensus algorithm (rules set by specific blockchains).
- Transaction is either accepted or rejected; if accepted, the transaction is added in chronological order along with other transactions to create a new block of data.
- Transaction is now a part of the Blockchain and is permanent and immutable.
There are several ways to build a blockchain. They can be public, private, hybrid, or consortium-built.
Blockchain layers refer to building multiple layers of blockchain on top of each other, where each layer can have its own consensus mechanism, rules, and functionality. This ensures better scalability, as transactions can be processed parallel across different layers.
Blockchain store information on monetary transactions using cryptocurrencies and information like product tracking and other data types.
We can create our Blockchain application. To do that, we can summarize it into the following steps:
- Step 1: Understanding Blockchain and its key components, i.e., having a fundamental grasp on blockchain concepts, its critical features like decentralization, consensus mechanisms (e.g., Proof of Work, Proof of Stake), immutability (once data is added, it cannot be altered), and cryptographic security.
- Step 2: Understanding the Purpose of your application, i.e., which use case or specific problem you want to address with your blockchain.
- Step 3: Creating a specific use case for your application that caters to particular needs will define target users that will determine the problems your application can solve and the benefits it will bring.
- Step 4: Research existing Blockchains related to your use case to determine if they exist. If it exists, you can build your application on top of it, saving time and resources while benefiting from the existing network and infrastructure security.
- Step 5: Choosing the right Blockchain platform for your use case, like, for example, Ethereum for smart contracts and decentralized applications, Hyperledger for enterprise-focused, Corda for financial applications, etc.
- Step 6: Select the consensus algorithm that will be used and best suited for your application requirements example Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS) etc.
- Step 7: Each Blockchain platform can have its programming languages. If you choose Ethereum, you must learn Solidity, a high-level programming language used to create smart contracts and decentralized applications on the Ethereum network. Also, you need to learn development tools like Truffle or Remix if you use Ethereum; Truffle provides an environment for testing, deploying, and managing smart contracts. Remix is a browser-based IDE that simplifies intelligent contract development and debugging.
- Step 8: Get an account or wallet on your chosen platform and buy their currency example Ether for Ethereum to deploy and interact with your smart contracts on the Ethereum. Purchasing the currency will help you to cover transaction costs and to test your application on the live network.
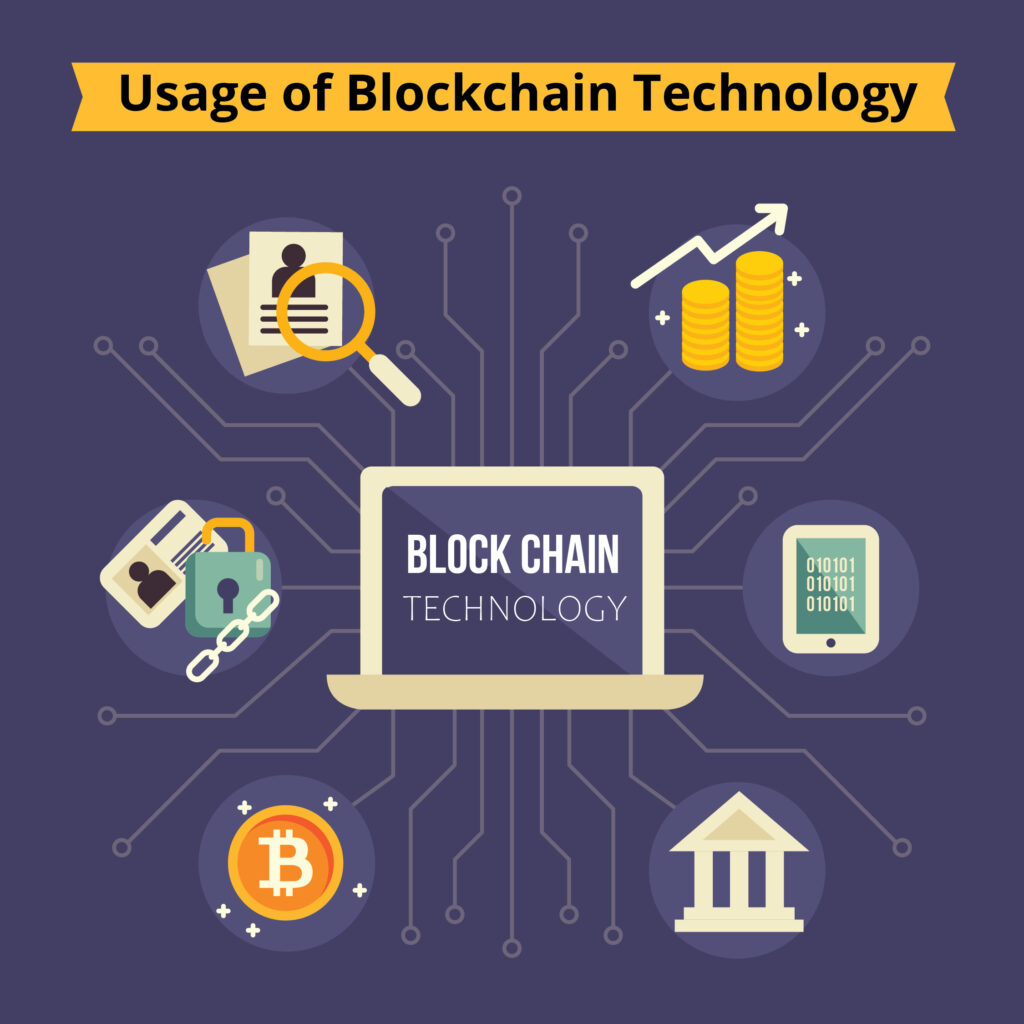
- Blockchain in Healthcare – Medical records can be stored on a decentralized ledger; it ensures data integrity and inoperability and enables seamless sharing of patient information across healthcare providers.
- Blockchain in Supply Chain Management – Blockchain can revolutionize supply chain management by enhancing transparency and traceability. It can track the movement of goods and materials as they change hands. Enables consumers to verify the origin and authenticity of products.
- Blockchain in Voting and Governance – Blockchain, a decentralized system, can be an ideal solution for voting and governance systems.
Blockchain holds immense potential but also faces several challenges. Regulatory frameworks and legal concerns surrounding cryptocurrencies and smart contracts require clarity and adaptation.
Despite challenges, research and developmental efforts are going on to address the problems in blockchain technology. As Blockchain continues to evolve and find new applications, it promises to unlock unprecedented opportunities for innovation and progress.














